Figure 4
Download original image
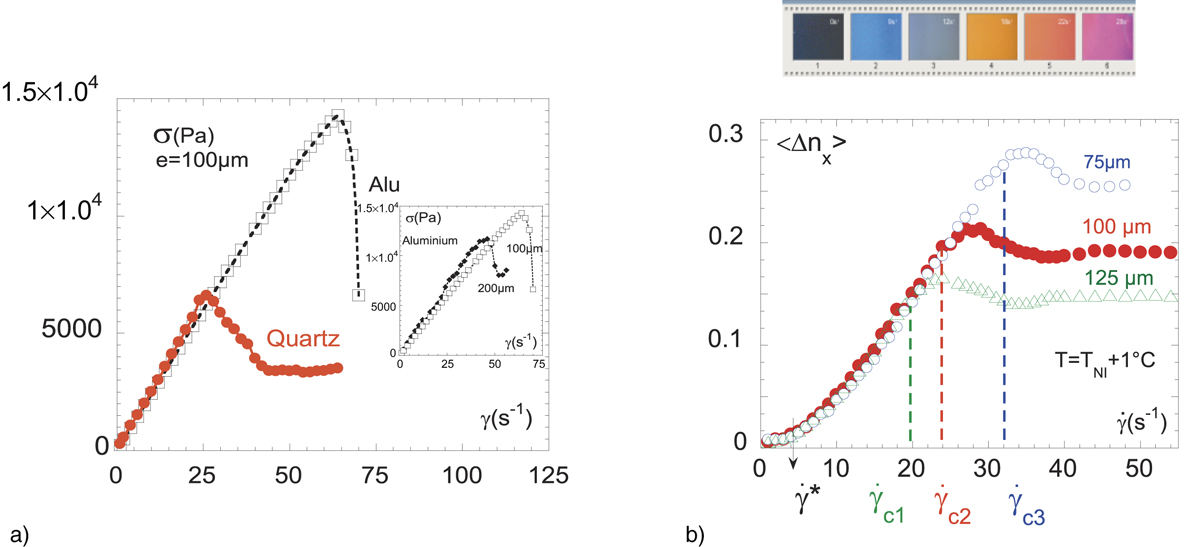
External parameters as the surface impact the flow. This is particularly visible at the sub-millimeter scale. The figures illustrate steady state flow behavior in the liquid (isotropic) phase of a low molecular weight liquid-crystal polymer (generic behavior) from [12]: a) shear stress versus shear rate measured on different substrates. In the Newtonian regime, shear stress and shear rate are proportional ![]() where η is the viscosity: red ● (100 μm): quartz substrate, □ (100 μm): aluminium substrate, at low shear rates (
where η is the viscosity: red ● (100 μm): quartz substrate, □ (100 μm): aluminium substrate, at low shear rates (![]() s−1 for the quartz and 70 s−1 for the aluminium substrate), the flow is linear to the shear rate (Newtonian regime). At higher shear rates, the departure from the linearity indicates a slippage transition which is a function of the force of the interactions to the substrate. In the inset, the shear stress versus shear rate is reported at 200 μm: Δ, and at 100 μm: □ (aluminium substrate). b) Flow birefringence < Δnx > versus shear rate at different gap thicknesses: (blue ○) 75 μm, (red •) 100 μm and (green △) 125 μm. Similarly, the occurrence of the birefringence plateau at high shear rates indicates a slippage at the surface. This slippage regime at constant shear rate depends on the sheared thickness as here illustrated.
s−1 for the quartz and 70 s−1 for the aluminium substrate), the flow is linear to the shear rate (Newtonian regime). At higher shear rates, the departure from the linearity indicates a slippage transition which is a function of the force of the interactions to the substrate. In the inset, the shear stress versus shear rate is reported at 200 μm: Δ, and at 100 μm: □ (aluminium substrate). b) Flow birefringence < Δnx > versus shear rate at different gap thicknesses: (blue ○) 75 μm, (red •) 100 μm and (green △) 125 μm. Similarly, the occurrence of the birefringence plateau at high shear rates indicates a slippage at the surface. This slippage regime at constant shear rate depends on the sheared thickness as here illustrated.

