Table 4
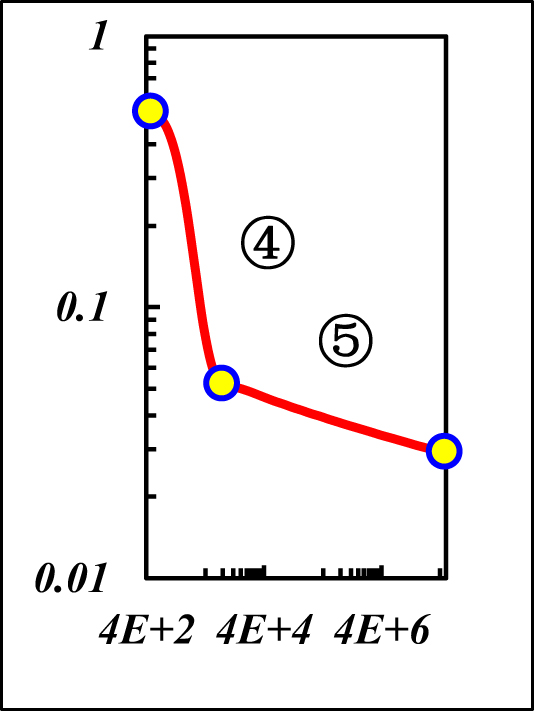
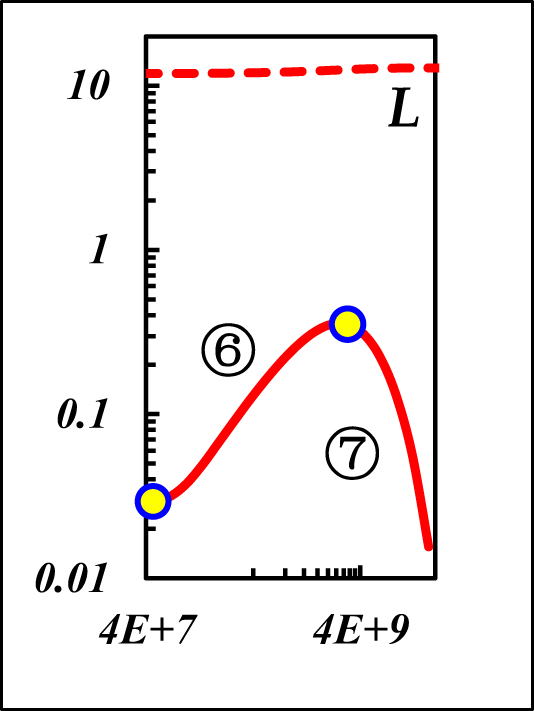
Boundary flow characteristics and pressure response behavior of Figure 6.
| Symbol description | Closed & const-pressure, r
eD
[Θ] < r
eD
[Ω] |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| κ[Θ] > κ[Ω] | κ[Ω] > κ[Θ] | |||
| Model sketch |
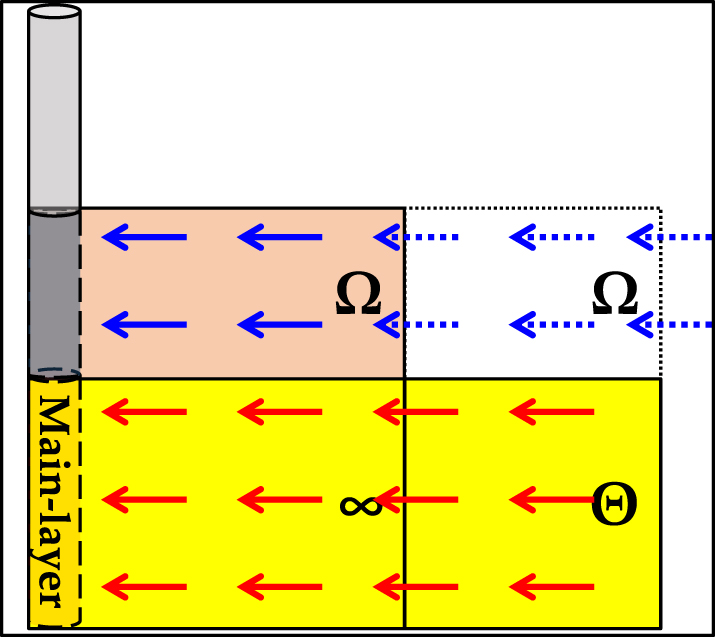
|
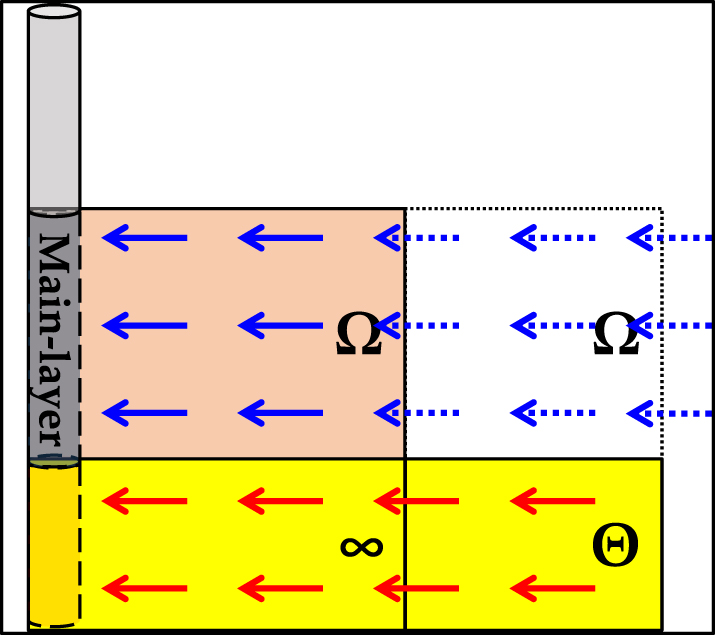
|
||
| Diagnostic curve |
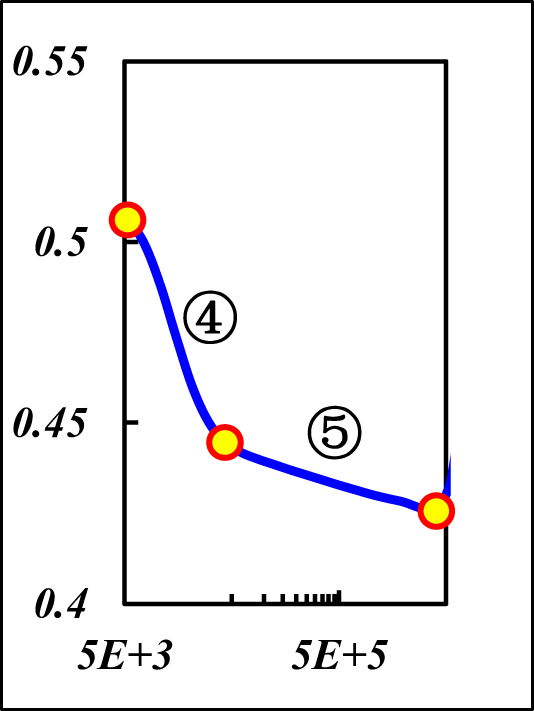
|
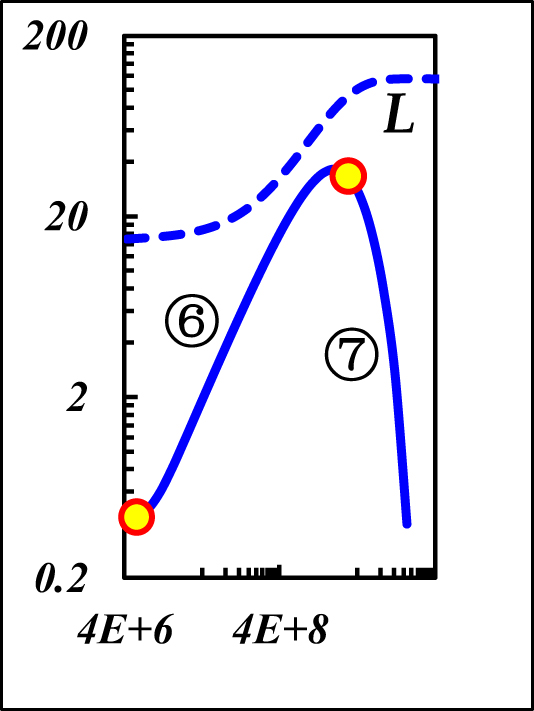
|
|
|
| Response behavior | The ④–⑤ is same as the boundary-domain flow of r eD [Ω] & r eD [∞] | |||
| The ⑥–⑦ is same as the boundary-domain flow of r eD [Ω] & r eD [Θ] | ||||
| ④Weak CpBF: const slope | ④Strong CpBF: const slope | |||
| ⑤Weak pseudo-CpBF: const slope m | ⑤Strong pseudo-CpBF: const slope m | |||
| ⑥Strong CBF: unit slope | ⑥Weak CBF: unit slope | |||
| ⑦Weak CpBF: const pressure L | ⑦Strong CpBF: const pressure L | |||
Notes: “CBF” is Closed Boundary Flow, “IARF” is the Infinite-Acting Radial Flow, and “CpBF” is the Constant-Pressure Boundary Flow. “Strong” indicates the boundary layer is the main-flow layer, and “Weak” indicates the boundary layer is the non-main-flow layer.

